The investment world is full of investing jargon that can leave you confused. Unfortunately, these investing terms you need to know intimidate most beginner investors from indulging in the investing world.
However, you don’t have to worry or think that investment is meant for the experts. The good news is that investment is quite simple when you have some knowledge of the common investing terms as well as simple tips for property investing.
Common investing terms you need to know
Whether you’re considering if now’s a good time to invest in property, or just brushing up on your investing vocabulary, let’s dive into the essential terms.
Asset allocation
Asset allocation refers to the administration of an investment strategy to balance risk and rewards. Usually, the asset allocation process involves distributing your securities in investment portfolios such as bonds, stocks, cash, commodities, and cash equivalents. This way, you don’t invest all your assets in one place.
Generally, asset allocation helps safeguard your money or securities and increase their growth potential, regardless of winning markets.
Rental Yield

Rental yield refers to the percentage of annual rental income earned from a property in relation to its total value. It is a straightforward measure that helps determine the potential profitability of an investment property.
By dividing the annual rental income by the property’s market value and multiplying by 100, rental yield provides a clear indication of the return on investment that can be expected from the property. In essence, rental yield is a simple and practical metric for evaluating the financial performance of a rental property.
The regions with the highest rental yield in Australia include Darwin NT and Fortitude Valley QLD.
Capital gain
Capital gain is the profit incurred after selling a property or investment. Usually, it’s the difference between the property net purchase price and the property net sale price.
On the contrary, a capital loss comes about when you sell a property for less than you bought it.
Mutual funds
Mutual funds refer to pools of money from various investors to purchase securities such as bonds, stocks, and other assets. A professional manager invests in the securities. Usually, the securities bought make up for the total amount of money pooled.
Additionally, each investor owns a share of the underlying asset, depending on how much they contributed to the mutual fund. Generally, a mutual fund is a safe investment program for any investor looking to retire.
Market Capitalization
Market capitalization refers to the current value of a company’s stock. To get the market cap of a particular company, you’ll need to multiply the price per share by the company’s total shares.
For example, for a company with 50 million shares and a cost per share of $5, the market capitalization is $250 million. Companies with high market capitalization are known as large-cap stocks.
Index funds

Index funds track the market’s underlying index performance. The funds allow investors to invest in indexes such as Nasdaq 100, Russell 2000, and S&P 500, among others.
Cash invested in an index fund is usually used as an investment in those companies with a particular index. Moreover, the returns are also in the specific index that’s invested.
For example, if you invest in Nasdaq 100, the returns are in Nasdaq 100. Generally, an index fund is a method of building passive wealth for long-term purposes. Additionally, investors who lack time to manage their portfolios and research stocks can invest in index funds.
Dollar cost averaging
Dollar-cost averaging refers to regularly investing an equal amount of money, regardless of how the market is doing. This is a great way to build an investing habit to achieve your financial goals in the long run.
Investment account
Investment accounts refer to accounts that hold cash, bonds, stocks, ETFs, and other securities. Usually, unlike bank accounts, the asset value in investment accounts often fluctuates – they can increase or decline.
Price to earnings ratio (P E ratio)
The price-to-earnings ratio calculates a company’s value. The P/E ratio evaluates a company’s stock price to per-share earnings. For example, if the company’s stock costs $30 per share and the company’s profit is $5 per share, then the price-to-earnings ratio is 6.
Hedge funds
A hedge fund refers to a private limited partnership of high-net-worth investors. Professionals manage investments through various high-end strategies to earn high returns.
Mostly, hedge funds’ investment activities are riskier compared to typical investments. Most importantly, hedge funds are available to investors with specific net worth.
Bear market and bull market
The terms bear and bull describe what’s happening (whether there’s a rise or fall) in the stock market. Usually, a bear market indicates a long period of economic decline (20%+ fall).
Generally, bears are negative, while bulls are positive. Usually, a bull market suggests a long period of economic growth (20%+ growth).
Net asset value (nav)

The NAV of a company is the value of the assets minus liabilities. For example, if a company’s total value of assets is $200 million and the liabilities are $30 million, then the company’s net asset value is $170 million.
Securities and exchange commission (SEC)
SEC is a government agency created to administer laws regulating security markets in the United States. These laws help promote fair dealing, thus protecting investors against fraud.
Dow Jones industrial average
Dow Jones Industrial Average refers to a stock market index consisting of the top 30 US largest companies listed on the stock exchanges.
Market Capitalisation
Understanding the market capitalization of major companies can be useful. For example, checking the CSL Limited Share Price and multiplying it by the total number of outstanding shares, investors can gauge the company’s total market value, offering insights into its size and significance in the market.
People also ask
What are the main types of long-term investments?
Long-term investment types include bonds, stocks, ETFs, mutual funds, cash equivalents, and real estate.
How do you start investing?
To start investing, you’ll need to open an investment account and link the investment account to a bank account for funds transfer. The funds are then invested in bonds, stocks, cash equivalents, and other securities to earn returns.
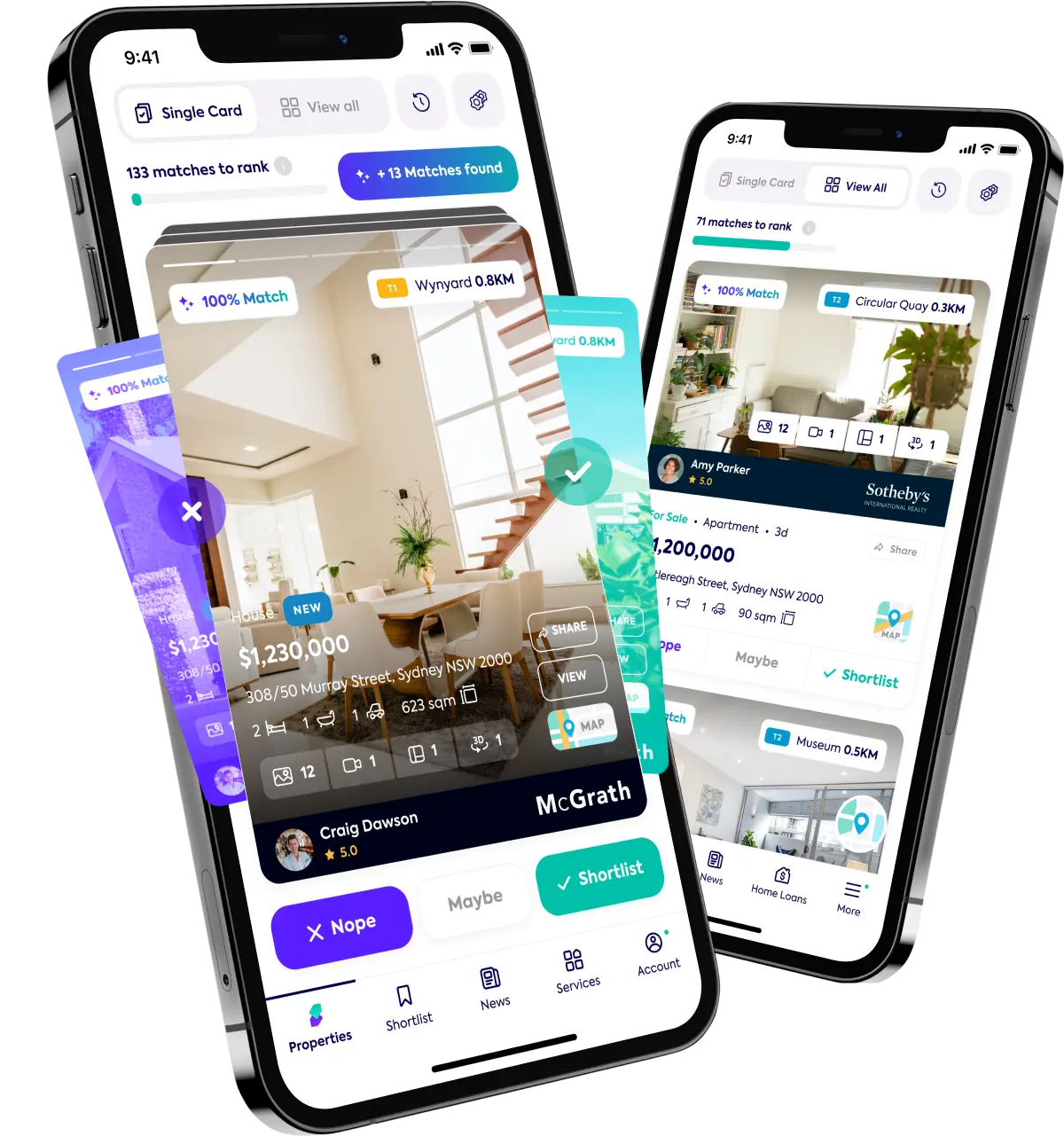
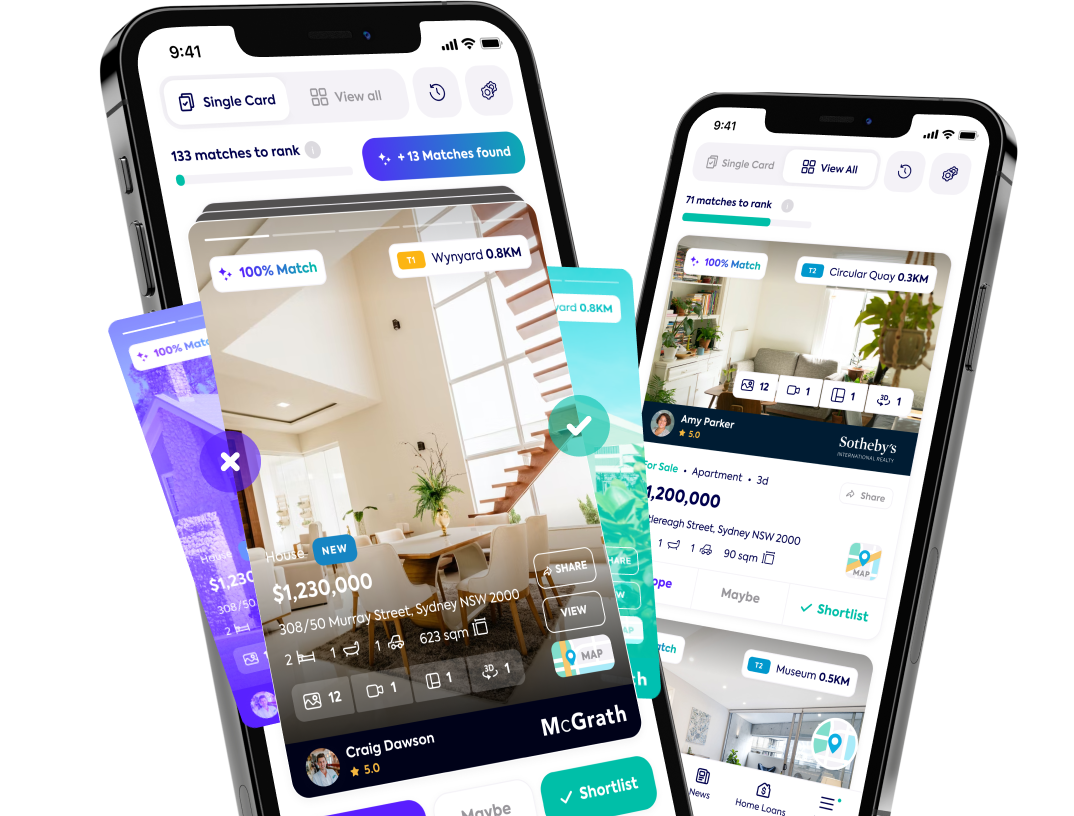
Looking for your investment home?
Knowledge of common investment terms is one step on the investment journey.
Next, you can express different investing concepts, which is important for every beginner and seasoned investor . It allows you to build confidence in the industry as you build your retirement account.
And when you’re ready to get your feet wet, explore our investment properties under $100k!
Soho can help you find it. Set up your profile on Soho to find properties for sale in your favourite suburbs. But don’t just stop there, download our app to get access to more features. Just remember to shortlist or swipe left on our listings so we can send you others that better match what you’re looking for.